|
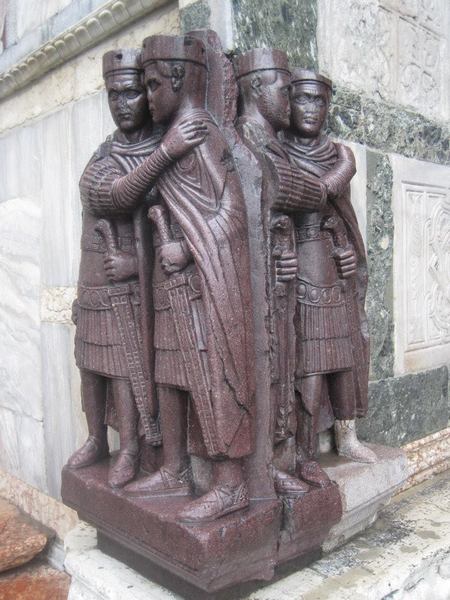
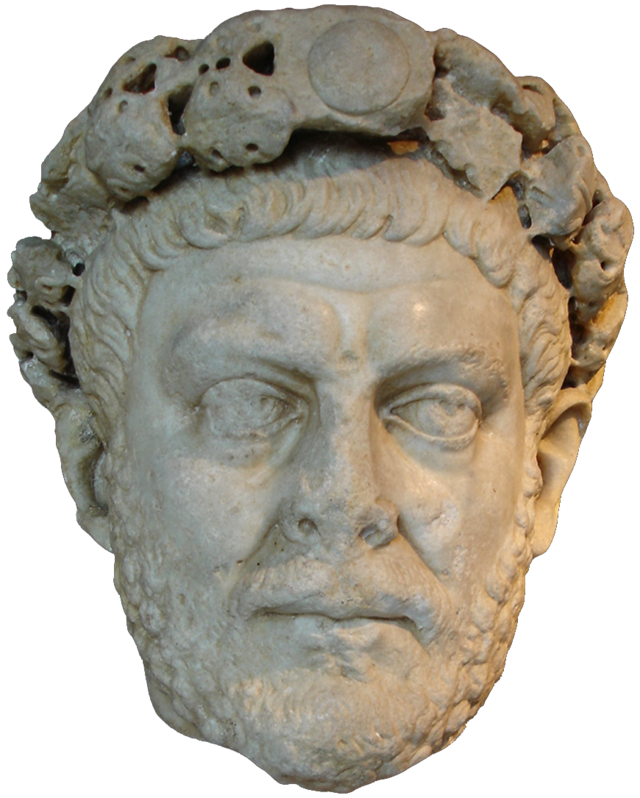
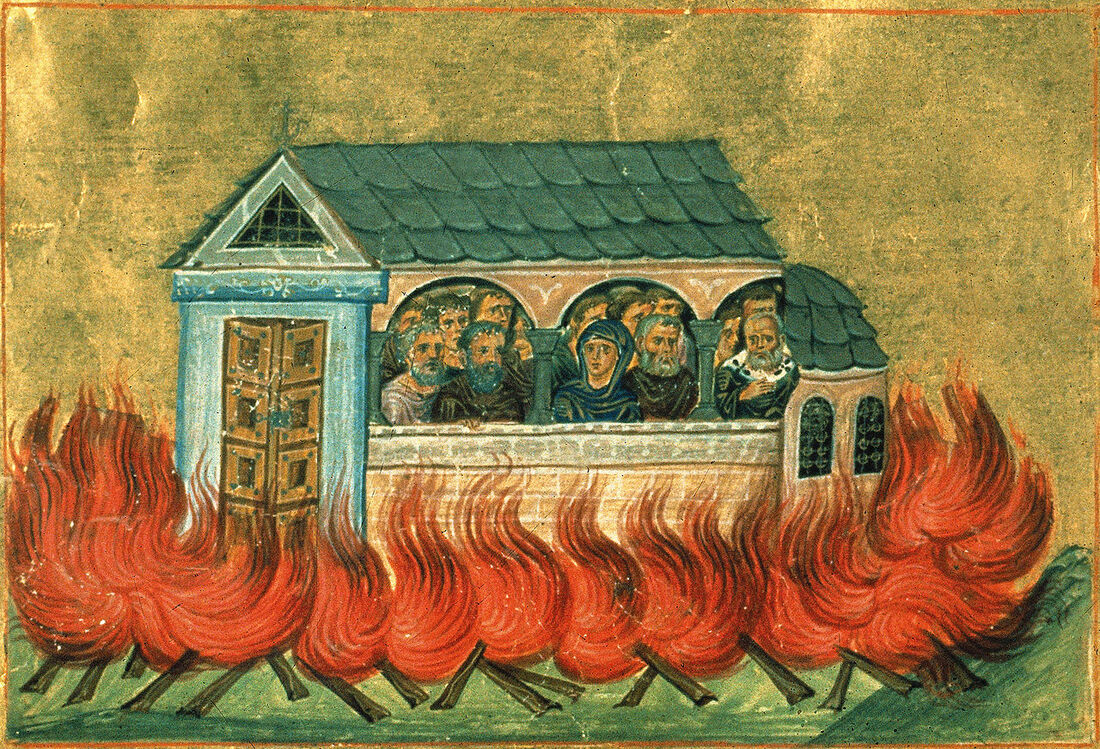
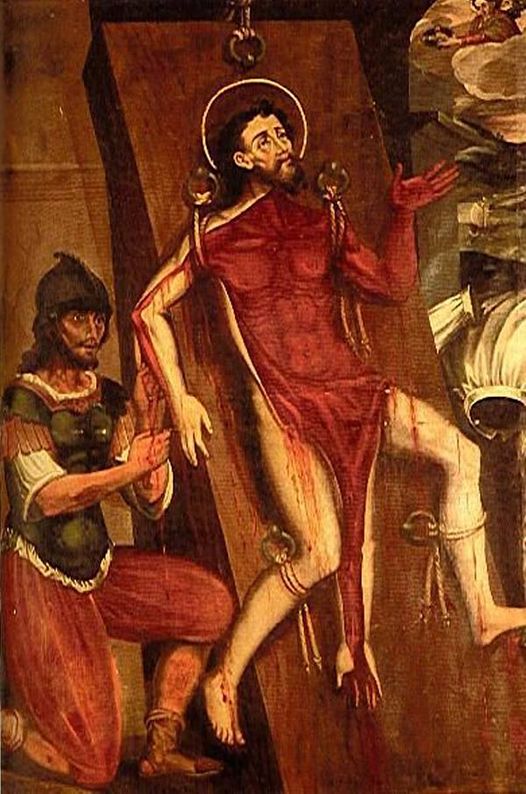
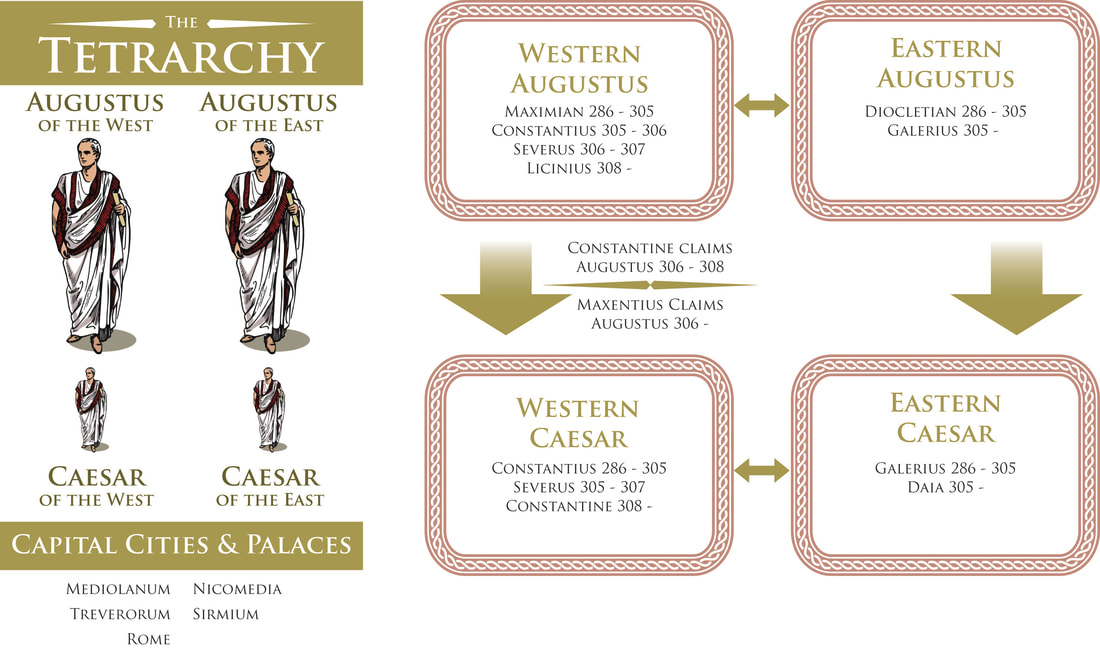
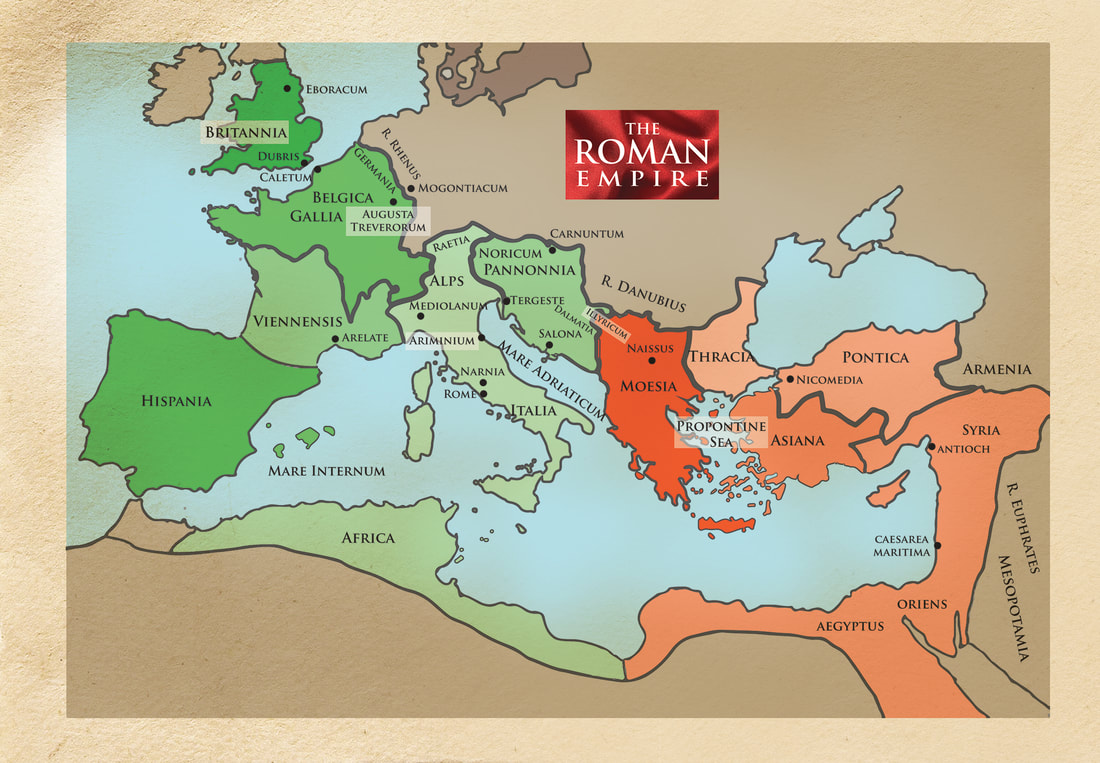
In the late 3rd century, the Roman Empire was a creaking mess. Riven by endless civil wars, succession struggles and splinter empires, the whole realm looked to be on the brink of disintegration. Along came Emperor Diocletian, who proposed a new system of rule: The Tetrarchy. Here, the empire would be split into more manageable Eastern and Western halves, with each half having an Augustus (a senior emperor) and a Caesar (a junior emperor). When an Augustus abdicated or died, his Caesar would step into his throne and appoint a Caesar of his own. And so on and so forth. No more wars of succession! ...yeah, right. Diocletian's vision was well-intended, but dreadfully executed. At the dawn of the 4th century AD he made one of his biggest mistakes by sponsoring the Great Persecution - a tyrannical pogrom of the empire's many Christians, led by himself and his Eastern Caesar, Galerius. Diocletian's complaint against the Christians was this: for centuries, the citizens of the Roman Empire had worshipped the old pantheon of Jupiter and the Olympian family. In doing so, they were also acknowledging and paying homage to the emperor himself, venerating him as the embodiment of one of those Gods. Indeed, Diocletian had a penchant for painting himself gold and insisting on being addressed as Jupiter. Citizens were expected to demonstrate their loyalty to Jupiter and thus to him by sacrificing animals. The Christians, however, did not believe in the sacrifice of any living creature. They also did not believe in worshipping their god 'via' an emperor. In the eyes of Diocletian, they lived their lives in the Roman Empire, but not as part of it. This would not do, and so the Great Persecution began. What came next was an age of public burnings and peelings, of riots and butchery across the empire's cities. It must be noted that much of the descriptive that follows comes from the Christian authors writing after this bleak time, and of course they were undoubtedly biased and keen to stress just what horrors their predecessors had been put through. It all began in a relatively gentle fashion with the legions. Soldiers seen making Christian gestures were blamed for imperial and military failures, and were summarily dismissed, losing their reputations and pensions. Things became bloody when Diocletian and Galerius were at the city of Antioch to witness a ceremony of sacrifice. The proceedings were interrupted by a loud and grating voice. The Deacon Romanus circled the ceremony over and over, denouncing the act. Diocletian ordered his arrest, first sentenced him to death, then changed his mind and ordered his tongue ripped out first. Returning to his Tetrarchic seat at the city of Nicomedia, Diocletian then set about formalising his dislike for the Christians. Egged-on by his underling, Galerius, he then issued what has come to be known as the First Edict of Persecution - a call to destroy all Christian buildings and scriptures and seize the faith's property and wealth. “ Diocletian recommended this should all be carried out without bloodshed. However, in practice - and overseen by Galerius - it was very different. Etius was one of the first to be martyred. Having torn down a copy of the edict in Nicomedia's forum, he was arrested and burnt alive. Burning happened to be Galerius' favoured way of dealing with the Christians. Indeed, one prominent Christian church in Nicomedia was soon after set ablaze while still packed with worshippers. Bishop Anthimos escaped the flames, only to be captured and beheaded. Shortly after this, the imperial palace caught light and the Christians were blamed. This, in a way, legitamised Galerius' brutality and so many more Christians were now hunted down, beaten and, yep, burned alive. In order to weed out hiding Christians, the tests of sacrifice were became mandatory and took place all across the Eastern Empire. After refusing to comply, Diocletian's butler, Peter, was hung by his wrists and had the skin peeled from his body. If that wasn't enough he was then "roasted on a gridiron".
Countless burnings, peelings, beheadings and more followed. These atrocities threw the empire into chaos: widescale riots and protests against the persecutions only led to retaliatory mob attacks on the rioters and further edicts that intensified the brutality. Into this bloody and fiery world, Constantine the Great was born. Sons of Rome tells the story of his rise during the days of the Persecution and of the Tetrarchy, and his days of friendship with Maxentius, son of a Western Augustus. A friendship that was not to last...
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorGordon Doherty: writer, history fan, explorer. My Latest BookArchives
March 2023
Categories |










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed